Car recycling is a crucial industry in the United States, playing a significant role in environmental conservation, resource management, and economic growth. As vehicles reach the end of their useful lives, the automotive recycling industry ensures that these machines are processed efficiently and responsibly.
Key Statistics
- As of 2019, there were 276 million vehicles in operation on US roads.
- Approximately 12-15 million vehicles reach the end of their life each year in the US.
- The auto recycling industry is the 16th largest in the US, contributing $32 billion in sales annually.
- The industry employs about 140,000 people at 9,000 locations nationwide.
- 95% of all vehicles that have reached the end of their lives are fully processed.
- Cars are the most recycled consumer product in the world, surpassing paper, aluminum cans, and glass.
The Importance of Vehicle Recycling
Environmental Benefits
- Reduces air and water pollution
- Saves energy in manufacturing new parts
- Reduces greenhouse gas emissions
- Prevents hazardous materials from entering the environment
Economic Impact
- Creates jobs in the recycling industry
- Provides affordable used parts for vehicle repairs
- Contributes significantly to the national economy
Resource Conservation
- Recycles over 14 million tons of steel annually
- Saves 85 million barrels of oil per year
- Reuses valuable materials like aluminum, copper, and precious metals
What Happens to a Recycled Car?
When a car reaches the end of its life, it goes through several stages:
- Evaluation and purchase by a recycling facility
- Removal of reusable parts
- Draining of fluids
- Removal of hazardous materials
- Crushing and shredding of the remaining shell
- Separation of materials for recycling
Composition of a Typical Car
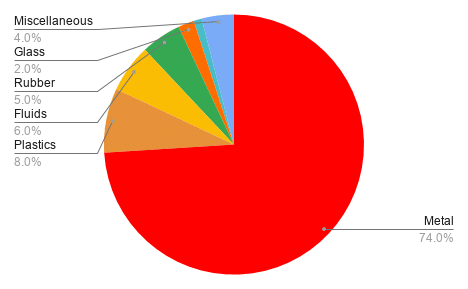 Understanding what a car is made of helps appreciate the recycling process:
Understanding what a car is made of helps appreciate the recycling process:
- Metal: 74%
- Plastics: 8%
- Fluids: 6%
- Rubber: 5%
- Glass: 2%
- Textiles: 1%
- Miscellaneous: 4%
The Future of Car Recycling
As vehicle technology evolves, so does the recycling industry. Current challenges and opportunities include:
- Recycling electric vehicle batteries
- Improving the recycling of automotive plastics
- Reducing the small percentage of materials that still end up in landfills
- Finding Innovative Uses for Recycled Car Parts
Conclusion
Car recycling in the United States is a thriving industry that provides significant environmental and economic benefits. As we continue to innovate in vehicle manufacturing, the recycling industry adapts to ensure that end-of-life vehicles are processed efficiently and sustainably, contributing to a cleaner, more resourceful future.
