What is a Junk Car? Definition, Characteristics, and Monetary Values
Junk cars represent the final chapter in a vehicle's lifecycle, serving as a vital but often overlooked component of the automotive ecosystem. These end-of-life vehicles—whether damaged, non-operational, or scrap—play a crucial role in the circular economy of transportation, providing a significant source of recyclable materials, reusable components, and sustainable waste management solutions.
The scale of the junk car industry is staggering. Approximately 15 million vehicles reach the end of their serviceable lives annually in the United States alone, nearly matching the 17 million new vehicles that enter the market each year. With an average junk car value of around $450, this creates an $8.1 billion industry that supports thousands of jobs in recycling, parts salvage, and metal processing sectors.
Despite common misconceptions that junk vehicles are worthless, these automobiles contain valuable metals, functional components, and recyclable materials that contribute significantly to resource conservation and environmental sustainability. From the steel in their frames to the platinum in their catalytic converters, junk cars are treasure troves of resources waiting to be reclaimed.
Whether you're facing the decision to repair or junk your aging vehicle, seeking the best disposal option for a damaged car, or simply curious about what happens to vehicles after they're no longer roadworthy, this comprehensive guide will navigate you through every aspect of junk cars. We'll explore their definition, characteristics, valuation factors, disposal methods, environmental impact, and the complex legal considerations that govern their handling.
By understanding the full lifecycle and value proposition of junk cars, vehicle owners can make informed decisions that maximize financial return while contributing to sustainable automotive practices. Whether your vehicle has been rendered undriveable by accident damage, mechanical failure, or simply the passage of time, this guide will serve as your definitive resource on navigating the end of your car's journey.
Definition and Basic Understanding
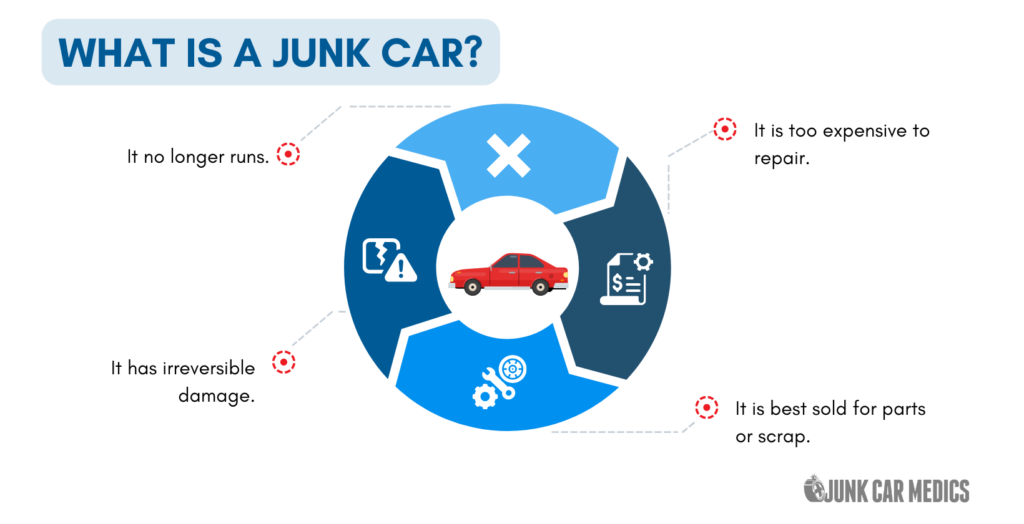
What is a Junk Car?
A junk car is a vehicle that has reached the end of its useful life due to age, damage, mechanical failure, or deterioration to the point where it is no longer safe or economical to operate. These vehicles typically have little to no value as functional transportation, but retain worth through their recyclable materials and potentially salvageable parts. Junk cars are characterized by their inability to be driven safely on public roads, their repair costs exceeding their market value, or their classification through legal designation such as a salvage title.
Common Terminology
The automotive world has developed various terms to describe vehicles in their end-of-life stage, each with subtle nuances in meaning:
- Scrap car: Emphasizes the vehicle's value primarily as recyclable material rather than as a functioning automobile.
- Clunker: Refers to an old, unreliable vehicle that may still run but is in poor condition and likely nearing the end of its useful life.
- Jalopy: A colloquial term for an old, decrepit car in poor condition, often with visible wear and mechanical issues.
- Hooptie: Slang term for an old, often larger car that is in poor condition but might still be drivable despite numerous issues.
- Beater: Describes a vehicle with significant cosmetic damage that is still operational but has minimal value beyond basic transportation.
- Salvage vehicle: Specifically refers to cars that have been deemed a total loss by insurance companies but may be repairable.
- End-of-life vehicle (ELV): The formal industry and regulatory term for vehicles that have reached the end of their useful life.
- Decrepit car: Emphasizes the severely deteriorated condition of an aged vehicle.
- Junker: Direct synonym for a junk car, focusing on its final disposition.
Example Scenarios
To better understand what constitutes a junk car, consider these real-world examples:
- "After John's 2003 Chevrolet Impala suffered engine failure at 245,000 miles, repair estimates exceeded $3,000—far more than the car's $1,200 market value, making it a junk car ready for scrap."
- "Maria's Toyota Corolla was declared a total loss after severe flood damage compromised its electrical systems, transforming a once-reliable vehicle into a junk car overnight."
- "Frank's 1998 Ford Explorer had accumulated so much rust that structural components were compromised, rendering it unsafe to drive and classifying it as a junk car despite its engine still running."
- "After sitting abandoned in Lisa's backyard for three years, her old Honda Accord had deteriorated to the point where rodents had damaged the wiring and fluids had leaked out, making it a classic example of a junk car."
- "Though Robert's truck still started, multiple failed emissions tests, worn-out suspension components, and extensive body rust qualified it as a junk vehicle in the eyes of the state's inspection program."
Legal Classification of Junk Cars
The legal definition of a junk car varies by jurisdiction, but typically involves one or more of these official designations:
- Title Status: Vehicles with salvage, junk, rebuilt, or non-repairable titles as classified by state DMVs.
- Municipal Ordinances: Local laws that define junk cars for the purpose of property maintenance codes, often including criteria such as:
- Non-operational status for a specified period (typically 30-90 days)
- Missing essential components (engines, wheels, etc.)
- Expired registration exceeding a certain timeframe
- Storage location (exposed to public view)
- Environmental Protection Regulations: Cars classified as waste or hazardous materials due to fluid leakage or improper storage.
- Insurance Designation: Vehicles declared a "total loss" when repair costs exceed a percentage of the car's value (typically 70-80%).
- Federal Definitions: The National Salvage Motor Vehicle Consumer Protection Act provides guidance for classifying vehicles with specific damage thresholds.
Many states require junk car buyers to maintain records of vehicle acquisition, including VIN numbers, purchase dates, and seller information, reinforcing the formal legal recognition of these vehicles' end-of-life status. In practical terms, a car may be considered legally "junk" when it fails to meet state inspection requirements, cannot be registered due to its condition, or violates local property codes related to inoperable vehicles.
Understanding these definitions and classifications helps vehicle owners navigate the disposal process and comply with relevant regulations when the time comes to part with a vehicle that has reached the end of its useful life.
Characteristics of Junk Cars
Age Factors
Age is one of the primary characteristics that define junk cars. Based on industry data, the average junk car is approximately 18 years old, reflecting the natural lifecycle of modern vehicles. This age threshold represents the point at which many vehicles have experienced sufficient wear to make continued operation impractical. These vehicles are often referred to as end-of-life vehicles.
Key age-related patterns include:
- Vehicles from model years 2000-2009 currently constitute the majority of junk cars processed
- The most common model year for current junk cars is 2006
- Luxury vehicles tend to reach junk status at a slightly older age (20+ years) due to higher initial build quality
- Economy vehicles often reach junk status earlier (15-17 years) due to lower-cost materials and construction
- The age threshold for junk classification has increased over decades as overall vehicle durability has improved
As vehicles age, they face increasing challenges with parts availability, rising maintenance costs, and incompatibility with modern safety and emissions standards, all contributing to their eventual classification as junk.
Mileage Indicators
Mileage serves as a crucial metric for identifying potential junk cars, with most junk vehicles having accumulated substantial odometer readings. Typical junk cars exhibit:
- Odometer readings exceeding 150,000 miles, with many reaching 200,000-300,000 miles
- Some well-maintained vehicles reaching junk status at 300,000+ miles
- Diesel engines often accumulating higher mileage before reaching junk status (often 300,000+)
- Commercial vehicles typically junked at higher mileage thresholds due to more robust construction
- Vehicles junked with lower mileage (under 100,000) typically due to accident damage or catastrophic mechanical failure
High mileage correlates with significant wear on major components including engines, transmissions, suspension systems, and interior elements, ultimately contributing to the economic infeasibility of continued operation.
Condition Assessment
Junk cars typically display multiple condition issues across several categories:
Mechanical Condition:
- Non-functional or severely compromised major systems (engine, transmission, electrical)
- Multiple system failures occurring simultaneously
- Repair costs exceeding 75% of the vehicle's market value
- Failed emissions or safety inspections with prohibitive repair estimates
Body Condition:
- Extensive rust affecting structural components
- Frame damage compromising vehicle integrity
- Collision damage affecting multiple body panels
- Water or fire damage to interior components
Safety Concerns:
- Compromised safety systems (airbags, brakes, steering)
- Structural issues affecting crash protection
- Outdated safety features compared to modern standards
- Potential environmental hazards from leaking fluids
Operational Status:
- Inability to start or run consistently
- Unsafe driving characteristics (handling, braking, acceleration)
- Excessive consumption of oil, coolant, or fuel
- Inability to maintain highway speeds or handle normal driving conditions
Each of these condition factors contributes to the overall assessment of whether a vehicle has reached junk status, with combinations of issues typically present in most junk cars.
Most Common Junk Car Years and Models
Current market data reveals patterns in the types of vehicles most frequently processed as junk cars:
Most Common Model Years:
- Vehicles from 2000-2009 represent the bulk of current junk car inventory
- 2006 models are currently the single most common year for junked vehicles
- Pre-2000 vehicles constitute a declining percentage of the junk car market
Most Frequently Junked Models:
- Honda Accord (4% of all junk cars)
- Nissan Altima (3%)
- Honda Civic (3%)
- Jeep Grand Cherokee (2%)
- Toyota Camry (2%)
- Chevrolet Impala (2%)
- Ford Escape (2%)
Brand Distribution:
- Domestic brands like Chevrolet and Ford represent the largest share due to their historical sales volume
- Japanese brands including Honda, Toyota, and Nissan make up a significant portion
- European vehicles appear less frequently but typically command higher scrap values
Vehicle Type Breakdown:
- Standard passenger cars: 70%
- Trucks and SUVs: 23%
- Vans and minivans: 7%
These patterns largely mirror historical sales figures, with adjustment for vehicle durability, parts costs, and susceptibility to specific mechanical failures.
Driveable vs. Undriveable Junk Cars
An important distinction exists between driveable and undriveable junk cars, affecting both their value and disposal options:
Undriveable Junk Cars:
- Cannot be safely operated on public roads
- Typically exhibit major mechanical failures (engine, transmission, braking systems)
- Often have severe structural damage or safety issues
- Require towing or flatbed transportation for removal
- Generally command lower values due to reduced parts salvageability
- Constitute approximately 65% of the junk car market
Driveable Junk Cars:
- Can still operate, but with significant limitations
- May start and run but fail to meet legal safety or emissions standards
- Often exhibit multiple warning signs of impending major failure
- Typically safe enough to drive short distances at low speeds
- Command higher values due to functional major components
- Constitute approximately 35% of the junk car market
- May qualify for "drive it in" bonuses from some junk car buyers
It's important to note that a driveable junk car remains a junk car; its operational status is temporary and precarious. As one junk yard operator aptly states, "A driveable junk car is just a breakdown waiting to happen." The distinction primarily affects logistics and valuation rather than the fundamental classification of the vehicle as having reached the end of its useful life.
Understanding these characteristics helps vehicle owners realistically assess their cars and make informed decisions about repair, continued use, or disposal through the junk car market.
Types of Junk Cars
While all junk cars share the common characteristic of having reached the end of their practical utility as transportation, they arrive at this status through different paths. Understanding these distinct categories helps in properly evaluating, handling, and processing these vehicles.
End-of-Life Vehicles (ELVs)
End-of-life vehicles represent the natural conclusion of a car's lifecycle after years of normal use and wear.
Key Characteristics:
- Typically older vehicles (15+ years) that have reached the end of their operational lifespan
- Gradual deterioration across multiple systems rather than catastrophic failure
- Accumulated issues across mechanical, electrical, and structural components
- Progressive decrease in reliability and increase in maintenance costs
- Often still technically drivable but economically impractical to maintain
Processing Considerations:
- Generally rich in salvageable parts due to natural, non-catastrophic aging
- High value for vintage-specific components for other aging vehicles
- Often contain original components that haven't been previously replaced
- Typically require less environmental remediation compared to damaged vehicles
ELVs represent the most common type of junk car, accounting for approximately 60% of vehicles entering the junk car market.
Accident/Totaled Vehicles
These vehicles enter the junk car stream after sustaining significant collision damage that renders them uneconomical to repair.
Key Characteristics:
- Structural damage that compromises the vehicle's integrity
- Insurance designation as a "total loss" (repair costs exceeding 70-80% of value)
- Often relatively newer than other junk car types
- Damage patterns typically concentrated in specific impact areas
- May have many undamaged components and systems
Processing Considerations:
- High value for undamaged components from the non-impact areas
- Require careful assessment for hidden damage to components
- Modern vehicles may contain valuable advanced technology components
- May contain deployable safety systems requiring specialized handling
- Often involve insurance documentation and specific titling requirements
Accident vehicles constitute approximately 15-20% of the junk car market and typically offer higher value for parts salvage, particularly for newer models.
Mechanical Failure Vehicles
These vehicles become junk cars due to catastrophic failure of major mechanical systems, making repairs economically unfeasible.
Key Characteristics:
- Catastrophic failure of critical components (engine, transmission)
- Repair costs significantly exceeding the vehicle's market value
- Often exhibit reasonable body and interior condition
- May have good secondary components unaffected by the primary failure
- Relatively clear failure diagnosis compared to other junk car types
Processing Considerations:
- Value lies in unaffected components and systems
- Typically require less environmental remediation than damaged vehicles
- Often contain valuable intact body panels and interior components
- May represent good candidates for parts vehicles in enthusiast markets
- Often junked at lower mileage than ELVs
Mechanical failure vehicles make up approximately 15-20% of junk cars and are particularly valuable in the parts market for their many salvageable components
Flood and Fire Damaged Vehicles
These vehicles enter the junk car market after exposure to water or fire, typically causing irreparable damage.
Key Characteristics:
- Extensive damage across multiple systems from a single catastrophic event
- Difficult-to-detect damage in electrical and electronic systems
- Potential for long-term corrosion and degradation even after repairs
- Safety concerns related to compromised structural integrity or airbag systems
- Often identified through insurance records or title branding
Processing Considerations:
- Require specialized environmental handling due to contamination
- Limited salvageable parts due to the nature of the damage
- Higher risk for processing facilities due to potential hazards
- May contain toxic materials resulting from fire or water contamination
- Often subject to strict title and disclosure requirements
These environmentally damaged vehicles represent approximately 5-10% of the junk car market and are generally the most challenging type to process safely.
Abandoned Vehicles
Abandoned vehicles become junk cars after being left unattended for extended periods, often on public property or private property without permission.
Key Characteristics:
- Neglected condition with multi-system deterioration
- Often missing documentation such as titles or registration
- Typically left in place due to mechanical failure or high towing costs
- Frequently subject to vandalism or parts theft while abandoned
- May present environmental hazards from leaking fluids or deterioration
Processing Considerations:
- Complex legal procedures for establishing ownership
- Special documentation requirements for processing
- Often lower in salvageable value due to stripped components
- May require environmental remediation due to exposure
- Frequently processed through municipal programs rather than private sales
Abandoned vehicles account for approximately 5-8% of junk cars and often involve government agencies in their processing.
Salvage Title Vehicles
These vehicles have been officially designated with a "salvage" title status by state authorities, typically after an insurance declaration of total loss.
Key Characteristics:
- Official designation through title documentation
- History of significant damage or other qualifying events
- Permanent record in vehicle history databases
- Failed or incomplete rehabilitation attempts
- Defined legal status that limits future use options
Processing Considerations:
- Subject to specific legal requirements for processing
- Documentation needs for proper transfer and disposal
- May have been partially repaired, affecting parts value
- Often younger than other junk car types with higher parts value
- May have transferable salvage title documentation requirements
Salvage title vehicles constitute approximately 10-15% of the junk car market and are distinguished primarily by their official designation rather than their physical condition.
Understanding these distinct categories helps junk car buyers, sellers, and processors approach each vehicle with appropriate expectations, handling procedures, and valuation methods. While there is often overlap between categories (e.g., a flood-damaged vehicle may also have a salvage title), the primary pathway to junk status significantly influences how the vehicle should be handled and valued.
Understanding Junk Car Value
The value of a junk car is not arbitrary but determined by a complex interplay of factors ranging from vehicle specifications to market conditions. Understanding these value determinants helps sellers set realistic expectations and potentially maximize their returns when disposing of end-of-life vehicles.
Factors Affecting Junk Car Prices
Vehicle Year, Make, and Model
The specific identity of a vehicle significantly impacts its value in the junk car market:
- Year: Newer vehicles typically command higher prices due to:
- More valuable and reusable components
- Higher-grade materials used in construction
- Greater demand for parts compatibility with vehicles still on the road
- Advanced technology components with salvage value
- Make and Model: Brand and specific model influence value through:
- Parts interchangeability across manufacturer's vehicle lines
- Popularity and continued presence on roads (creating parts demand)
- Reputation for durability affecting component resale value
- Presence of high-value components specific to certain models
- Desirability: Some vehicles maintain higher value due to:
- Cult status among enthusiasts (creating specialized parts markets)
- Rarity of certain components
- Historically high failure rates of specific components creating demand
A 2015 vehicle will typically be worth substantially more than a 2000 vehicle of the same model, while popular models like Honda Accords and Toyota Camrys generally command premium prices due to their abundant presence on roads and continued parts demand.
Vehicle Condition and Weight
Physical characteristics directly affect salvage value:
- Condition Assessment:
- Vehicles with working engines and transmissions typically command $200-400 more
- Complete vehicles with all major components intact receive higher offers
- Extent of rust and corrosion (affecting metal quality and parts usability)
- Presence of all wheels and tires (each worth $10-25 in scrap value alone)
- Vehicle Weight:
- Heavier vehicles contain more recyclable metal
- Typical passenger car: 2,400-3,000 pounds
- SUV/light truck: 4,000-5,000 pounds
- Value calculated at approximately $180-220 per ton of metal
- Weight becomes the primary valuation factor for extensively damaged vehicles
A complete, running SUV might be valued $400-600 higher than a stripped, non-running compact car simply based on weight and operational status.
Current Scrap Metal Prices
The volatile commodities market directly impacts junk car values:
- Market Fluctuations:
- Scrap steel prices can vary 30-40% annually
- Prices typically range from $120-240 per ton
- Values track with global steel demand and production
- Prices affected by tariffs, international trade policy, and economic conditions
- Metal Content Value:
- Steel (average 2,090 lbs per vehicle): approximately $177 value at current rates
- Aluminum (average 416 lbs): approximately $100 value
- Copper & brass (average 39 lbs): approximately $129 value
- Platinum group metals (minimal amounts): approximately $180 value in catalytic converters
When scrap prices are high, the base value of all junk vehicles rises accordingly, while market downturns can reduce offers by 20-30% across the board.
Parts Value
Functioning components often represent the highest value in a junk car:
- High-Value Components:
- Engines (functional): $300-1,000 depending on type and condition
- Transmissions: $200-600 based on type and functionality
- Catalytic converters: $50-300 depending on type and precious metal content
- Electronic modules: $50-200 for functional units
- Body panels (undamaged): $50-300 depending on vehicle type
- Special Considerations:
- Rare or difficult-to-find parts can command premium prices
- Late-model electronic components maintain higher value
- Luxury vehicle components typically worth 30-50% more than economy equivalents
- Parts supply and demand affected by vehicle's continued presence on roads
A relatively new vehicle with a blown engine might still be worth $800-1,200 for its parts value alone, while an older vehicle might be valued primarily on its metal content.
Location
Geographic factors significantly impact junk car values:
- Regional Market Variations:
- Urban areas typically offer higher prices due to competition and infrastructure
- Rural areas may see lower offers due to transportation costs to processing facilities
- States with high concentrations of auto recyclers tend to offer better rates
- Proximity to metal processing facilities impacts base scrap value
- Environmental Regulations:
- Stricter state regulations can increase processing costs, lowering offers
- Variations in title and processing requirements affect buyer operational costs
- Some states subsidize vehicle recycling, potentially increasing offers
A junk car in Los Angeles might receive offers $100-200 higher than an identical vehicle in rural Nevada due to proximity to recycling infrastructure and competitive market conditions.
Title Status
Documentation significantly impacts both value and salability:
- Clean Title:
- Vehicles with clean, available titles typically command $100-300 more
- Simplifies processing and reduces administrative costs for buyers
- Allows for potential parts car sale rather than immediate scrapping
- Missing Title:
- Reduces value by $100-300 due to administrative complexity
- May make the vehicle unsalable in some jurisdictions
- Requires additional documentation and processing steps
- Salvage/Rebuilt Title:
- May reduce offers by 10-20% compared to clean titles
- Indicates previous significant damage, potentially affecting parts value
- Requires additional verification steps for processing
A vehicle with a clean, available title will consistently receive higher offers than an identical vehicle with title issues.
Price Ranges
Junk car values typically fall within predictable ranges based on condition and market factors:
- $50-200 Range:
- Older vehicles (pre-2000)
- Extensively damaged or incomplete vehicles
- Vehicles without titles in strict documentation states
- Smaller vehicles with low metal content during low scrap price periods
- $200-600 Range (80% of junk cars):
- Average condition vehicles 15-20 years old
- Complete but non-running vehicles
- Vehicles with moderate damage but salvageable parts
- Average weight vehicles during moderate scrap price periods
- $600-1,500 Range:
- Newer vehicles (less than 15 years old)
- Vehicles with functioning major components
- Popular models with high parts demand
- Heavier vehicles during strong scrap price periods
- $1,500-5,000 Range:
- Late model vehicles (less than 10 years old)
- Vehicles with minimal damage but expensive mechanical failures
- Luxury or specialty vehicles with high-value components
- Vehicles with collectible or rare components
The majority of junk cars (approximately 80%) fall into the $200-600 range, with outliers at either end of the spectrum depending on the factors previously discussed.
Current Market Trends
The junk car market experiences both cyclical and long-term trends affecting values:
Recent Developments:
- Current scrap metal values are at relatively high levels compared to five-year averages
- Catalytic converter prices have risen substantially due to precious metal value increases
- Parts shortage for new vehicles has increased demand for used components
- Supply chain disruptions have elevated the value of readily available used parts
Seasonal Patterns:
- Higher prices typically offered in spring and summer months
- Winter often sees 5-15% lower offers due to reduced recycling activity
- End-of-quarter periods may see higher offers as recyclers meet volume targets
Long-Term Trends:
- Increasing vehicle longevity is raising the average age of junked vehicles
- Growing complexity of vehicles is increasing the value of electronic components
- Rising use of aluminum and composite materials is changing the scrap value equation
- Environmental regulations are becoming more stringent, affecting processing costs
Emerging Factors:
- Electric vehicle components introduce new value calculations
- Battery recycling is becoming a significant value component
- Advanced driver assistance components create new parts markets
- Digital marketplace platforms are increasing price transparency and competition
Understanding these value factors, ranges, and trends allows junk car sellers to set realistic expectations and potentially time their sales to maximize returns. While individual vehicle characteristics remain the primary determinants of value, market conditions and location significantly influence the final offers received.
When to Junk Your Car
The decision to junk a vehicle often becomes apparent through several key indicators:
- Repair costs consistently exceed the vehicle's market value
- Major component failure (engine, transmission) in an older vehicle
- Extensive rust affecting structural integrity
- Failed safety or emissions inspections with prohibitive repair costs
- Frequent breakdowns affecting reliability
- Difficulty finding replacement parts due to vehicle age
Cost-Benefit Analysis: Repair vs. Junking
When deciding whether to repair or junk your vehicle, consider this simple framework:
- Compare repair costs to the vehicle's current market value
- Factor in likely future repairs based on vehicle age and condition
- Consider diminishing returns on investment in aging vehicles
- Evaluate monthly repair costs against potential replacement vehicle payments
- Account for hidden costs like towing fees, rental cars during repairs, and lost time
Calculation Method for Determining When to Junk
Use this straightforward calculation to make an objective decision:
- Determine your vehicle's current market value (use Kelley Blue Book or similar)
- Get repair estimates for all current issues
- Add estimated costs for maintenance needed in the next year
- If repair/maintenance costs exceed 50% of the vehicle's value, junking is typically more economical
- For vehicles over 12 years old, reduce this threshold to 30% of value
Safety Considerations
Never compromise safety when deciding whether to keep an older vehicle:
- Structural rust can compromise crash protection
- Worn suspension components affect handling and braking
- Older vehicles lack modern safety features (advanced airbags, stability control)
- Intermittent electrical issues may affect critical safety systems
- Brake system deterioration increases stopping distances
Environmental Factors to Consider
The environmental impact of your decision works both ways:
- Older vehicles typically produce more emissions than newer models
- Manufacturing new vehicles requires substantial resources and energy
- Properly recycled vehicles recover up to 80% of materials
- Fluid leaks from deteriorating vehicles can contaminate soil and water
- Newer vehicles offer improved fuel efficiency, reducing lifetime carbon footprint
When multiple factors point toward junking, it's often the most practical, economical, and environmentally responsible decision for vehicles that have reached the end of their useful lives.
Disposal Options for Junk Cars
Sell to a Junkyard or Junk Car Buyer
The most straightforward disposal method for junk cars involves selling directly to specialized buyers:
- Process: Contact buyers for quotes, provide vehicle details, arrange pickup
- Advantages: Quick cash payment, free towing services, minimal paperwork
- Considerations: Offers vary significantly between buyers; research multiple options
- Typical Returns: $200-600 for most vehicles
- Time Investment: 1-3 days from initial contact to completion
Recycle at a Scrap Yard for Metal
Focusing purely on the metal value provides another disposal path:
- Process: Transport vehicle to scrap yard, complete transfer paperwork
- Advantages: Environmentally responsible, transparent pricing based on weight
- Considerations: May require self-transport or towing expense
- Typical Returns: $150-400 based on vehicle weight and current metal prices
- Time Investment: Same-day completion once vehicle is delivered
Donate to Charity
Vehicle donation offers both community benefit and potential tax advantages:
- Process: Contact qualifying charity, arrange pickup, receive donation documentation
- Advantages: Tax deduction possibility, supports charitable causes, free removal
- Considerations: Actual tax benefit depends on how charity uses vehicle
- Typical Returns: Tax deduction value varies by vehicle and charity's use
- Time Investment: 1-2 weeks from contact to documentation receipt
Sell to a Private Buyer
Direct sales to individuals can maximize return for salvageable vehicles:
- Process: Advertise through marketplace sites, arrange showing, complete sale paperwork
- Advantages: Potentially higher returns, especially for vehicles with usable parts
- Considerations: Requires more effort, possible safety and transaction concerns
- Typical Returns: $300-1,200 depending on vehicle condition
- Time Investment: 2-4 weeks average time to find buyer and complete sale
Trade-In at a Dealership
Using a junk car as credit toward a replacement offers convenience:
- Process: Bring vehicle to dealership, negotiate trade value, apply to purchase
- Advantages: Streamlined process combined with new vehicle purchase
- Considerations: Typically lower value than other options, requires purchase
- Typical Returns: $100-500 applied to new vehicle purchase
- Time Investment: Same-day completion as part of vehicle purchase
Government Options & Incentives
Some jurisdictions offer programs to remove older vehicles from roadways:
- Process: Apply through local environmental agency, follow program requirements
- Advantages: Potential cash incentives beyond vehicle value, environmental impact
- Considerations: Limited availability, specific vehicle qualification requirements
- Typical Returns: Base vehicle value plus $500-1,500 in incentives where available
- Time Investment: 3-8 weeks for application processing and program completion
Industry Statistics and Trends
Geographic Distribution
The junk car industry follows clear geographical patterns, with volume closely correlating to population density and vehicle ownership rates:
Top States for Junk Cars:
- California (15% of national volume)
- Texas (10%)
- Florida (7%)
- Pennsylvania (5%)
- Arizona (4%)
- Ohio (4%)
- Tennessee (3%)
Top Cities for Junk Car Processing:
- Los Angeles (4% of national volume)
- Chicago (3%)
- New York City (3%)
- Phoenix (2%)
- Houston (2%)
- Dallas (2%)
- Philadelphia (2%)
These distributions reflect both population centers and the influence of climate factors, with extreme weather regions (hot/humid South, salt-affected Northeast) seeing higher vehicle deterioration rates.
Most Common Junk Car Brands and Models
The most frequently junked vehicles largely mirror historical sales patterns with adjustments for durability:
Top Junk Car Brands:
- Chevrolet
- Ford
- Honda
- Nissan
- Toyota
- Dodge
- Jeep
Most Common Junk Car Models:
- Honda Accord (4% of all junked vehicles)
- Nissan Altima (3%)
- Honda Civic (3%)
- Jeep Grand Cherokee (2%)
- Toyota Camry (2%)
- Chevrolet Impala (2%)
- Ford Escape (2%)
Vehicle Type Distribution:
- Passenger cars: 70%
- Trucks & SUVs: 23%
- Vans & minivans: 7%
The 2000-2009 model years currently represent the bulk of vehicles entering the junk stream, with 2006 being the single most common model year processed.
Seasonal Trends
The junk car industry experiences predictable seasonal patterns affecting both volume and pricing:
Spring/Summer (April-August):
- 15-20% higher processing volume
- 5-10% higher average prices
- Peak vehicle replacement period
- More favorable weather for vehicle removal
Winter (December-February):
- 10-15% lower processing volume
- 5-15% lower average prices
- Reduced recycling facility activity
- Transportation challenges in snow-affected regions
End-of-Quarter periods often see increased buying activity as recyclers meet volume targets and quotas.
Market Price Fluctuations
Junk car values fluctuate based on several interconnected market factors:
Scrap Metal Prices:
- Historical range of $120-240 per ton for scrap steel
- 30-40% annual price variation typical
- Correlation with manufacturing demand and construction activity
- Influence of international trade policies and tariffs
Precious Metal Values:
- Catalytic converter prices fluctuate with platinum, palladium, and rhodium markets
- Can represent $50-300 of a vehicle's junk value
- Experienced 200%+ price increases in recent years
Parts Demand:
- Supply chain disruptions increase used parts value
- Vehicle shortage situations enhance salvageable component prices
- Older vehicle maintenance needs drive specific parts markets
Future Projections
The junk car industry faces several transformative trends in coming years:
Vehicle Composition Changes:
- Increasing aluminum content (projected 25% increase by 2030)
- Greater plastic and composite material usage
- Changing value proposition from weight-based to component-based
Electric Vehicle Impact:
- Battery recycling infrastructure development
- New valuation models for EV components
- Specialized handling requirements for high-voltage systems
Digital Marketplace Evolution:
- Online platforms increasing price transparency
- AI-driven valuation models improving accuracy
- Direct-to-consumer models bypassing traditional junkyards
Regulatory Changes:
- Stricter environmental standards for recycling processes
- Extended producer responsibility programs
- Potential incentive programs for removing older vehicles
These industry statistics and trends provide context for understanding the junk car market's dynamics and its evolution as vehicle technology and recycling practices advance.
Resources and Tools
Resources:
Tools:
- Junk Car Medics Calculator - Specialized tool for estimating junk car values
- Scrap Metal Price Indexes - Sites like Scrap Register track current metal values
- DMV.org - Comprehensive state-by-state guide to titling requirements
- Title Transfer Requirement Checklist - State-specific documentation needs
- EPA Vehicle Recycling Guidelines - Federal standards for vehicle disposal
